Programming Language (Low level, High level, 4 GL)
A vocabulary and set of
grammatical rules for instructing a computer to perform specific task is called
programming language.
Programming: The process of writing code for computer in order
to perform the specific task is called programming.
v Features of a
good programming language
·
Integrity:
- The calculation used in the program should very accurate.
·
Clarity: - The program should be well readable to aid
maintenance.
·
Simplicity:
- The program should be able to express the logic in a considerably simple way.
·
Efficiency:
- The program should have a good compromise between time and space used.
·
Modularity:
- Program should be separated to different logical and self-contained modules.
·
Generality:
- The program should be as general as possible within certain limits.
·
Robustness:
- Program must be fault-tolerant as much as possible.
Security: - a program must be secured enough so as to avoid tampering from
unwanted people.
Low level Language
Languages that are
closer to hardware or machines are called Low Level Language. These languages
are machine dependent; they depend upon the internal structure of the machine.
There are two types of low level language. They are: -
a) Machine level
language b)
Assembly level
language
a)
Machine Level Language:-
Machine level language is the language that is
directly understood by a computer. In other words, the set of binary digits (0
& 1) is the machine level language. Any information or instructions in this
language is represented in terms of 0 & 1. The symbol 0 stands for “off” or
the absence of an electric pulse and 1 stands for “on” or the presence of an
electric pulse.
Writing a program in a machine level language is
a very difficult process. For each instruction different codes are used. The
programming codes in a machine language depend upon the hardware of computer.
Thus, it is very difficult to write and modify the instructions in a machine
level language.
Advantages of
machine level language:
1)
It is more
efficient than other computer languages.
2)
It is directly
understood by computer.
Disadvantages of machine level
languages:
1)
Machine
languages are machine oriented.
2)
Difficult to
write programs and edit.
3)
Time consuming
to write programs.
b)
Assembly Level Language: -
The difficulties faced while writing a
program in a machine language led to the development of assembly language. It
uses symbolic notations to represent the instructions of the machine language.
These symbolic notations are called mnemonic codes. For example, ADD for
addition, SUB for subtraction etc.
The program written in assembly language
is called source program. Source program translated into machine language by a
translator program is called object program. Computer viruses are mostly
written in Assembly language.
Source
Program=>Assembler=>Object Program
1)
Simple to
understand and use than machine language.
2)
Easy to write
programs.
3)
Easier to debug
programs than the programs of machine language.
Disadvantages
to Assembly Level Language:
1)
It is low level
language so knowledge of hardware is required.
2)
Programming is a
lengthy and time consuming process in assembly level languages.
HIGH LEVEL
LANGUAGE:
It is purely problem oriented rather
than machine oriented. Easy to define program logic with reference to syntax
and extensive vocabularies like English Words. The high-level language code is
not directly executable. It requires translators like interpreter or compiler.
The
first high level language developed is FORTRAN (in 1956).
Advantages of High Level Language:
- They are machine
independent.
- They require
less time to write.
- Debugging is
easier in high level language.
- Better
documentations is provided by high level language
Disadvantages of High Level Language:
- Programs take more time to execute and require more money.
- Programs are not as written in machine level language.
4 GL (4th Generation Language):
Lying
above high level languages are called 4 GL. 4 GL is far removed from machine
languages and represent the class of computer languages closest to human
languages.
Compiler,
Interpreter and Assembler
- a) Assembler:-
b) Compiler:-
A compiler is a program which translates a high level program to machine language at once.
c) Interpreter:-Interpreter is a program which translates a statement of high level language program to machine language.
Differences between Compiler and
Interpreter
Compiler
|
Interpreter
|
1. a compiler is a program
which translates a high level program to machine language at once.
|
1. Interpreter is a program
which translates a statement of high level language program to machine
language.
|
2. Program execution time is
more before producing executable program.
|
2. It can execute immediately.
|
3. It occupies larger part of
memory.
|
3. It occupies less memory
space because it is smaller program in comparison to compiler.
|
4. It is faster because it runs
executable programs.
|
4. It is slower because it
repeats the process from the beginning.
|
5. Examples: C, C++,FORTRAN
etc.
|
5. Examples: BASIC, LISP etc.
|
List of High Level Language
- FORTRAN (Formula Translator)
- COBOL (Common Business Oriented Language)
- VISUAL BASIC (VB)
- JAVA
- C: - C was developed by Dennis Ritchie at Bell lab in USA. It has some low level languages features included in it to allow direct control of computer hardware.
Difference between Program and
software
Program
|
Software
|
1. A collection of
instructions that performs certain tasks and is written in the form of
computer language is called Program.
|
1. A set of
instruction given to the computer in machine code that tells to the computer
what to do and how to perform the given task of the user is called Software.
|
2. The main objective
of program is to make software for general or specific purpose.
|
2. The main objective
of software is to enhance the performance capability of hardware.
|
3. Examples: -
Finding total, percentage, division and result of students in college.
|
3. Examples:- Windows
XP, MS-Excel, MS-Access etc.
|
Concept of Programming statement
While
writing a program, we can use different statements or keywords. Each
instructions or statement begins with a reserved word called keywords. Rules of
particular keyword must be followed while writing a statement, which is called
syntax.
Syntax
and Programming Error
If any program contains any mistake due
to violation rules of programming language then it is said to be errors or
bugs. The process of findings bugs is called debugging. Mainly there are three
types of errors in program: syntax Errors, Logical (Semantics) Errors and
run-time error.
Syntax
Error: -
A
syntax error is occurred due to the violation of syntax of a programming
language. The key words and the structure of the instructions must be in
correct form. A syntax error is very easy to debug because compiler itself
detects syntax error and also describes the causes of the errors. So a
programmer does not need to trace errors. For Example : if we write the
spelling for printf is written pritf , this is a syntax error in C
programming.
Logical
Error (Semantics error): -
A
logical error is occurred due to the violation of semantics of a programming
language. It is also called semantics
errors. A compiler does not detect the logical errors therefore they are
very difficult to find out. The actual output does not come as per the given
data therefore; sample data are supplied to the program to examine the logic
errors. For example: if we decide to find the rank of student in a test
according to their percentages and if two students obtained the same percentage
(%) then , there may program get confused and occur a logical error.
Run-time Error:
A run time errors occur during the running time
of the software. This kind of error is occurred due to the problem of system or
mishandling of the software. Anytime run time error might be occurred so a good
programmer has to handle the errors using different error handling mechanism
during software development time. For example: Crashing of a program during
working on that software is a run time error.
Data type in C
language:
The
basic element of any program, which describes the nature of variables is called
data type .Data types are mainly used to define the type and nature of data
such that compiler detects and proceeds.
Data
types used in C are as follows:
1. Int: -
int is the keyword for integer. It contains the whole numbers between -32,768
to 32,767. It requires 2 bytes memory and its type specifier is %d.
Examples:
- int a=10;
2. Float: -
float is the keyword for floating numbers i.e. decimal numbers. It contains
number 3.4e – 38 to 3.4e+38. It requires 4 bytes memory and its type specifier
is %f. Example: - float pi=3.14;
3. Char: -
char is the keyword for character. It represents the single alphabet. It
requires 1 byte memory and its type specifier is %c. Example: - char choice;
4. String:
- The collection of character is called string. It is enclosed within double
quote. Its type specifier is %s. Example: Char str= “Computer”;
# Operator, Operands and Operation:
A
symbol that instructs C to perform some operation on one or more operands is
called Operator. The data on which
operator are performed is called Operand.
The result which we obtained after the work is done according to the operator
is called Operation.
For
example:
p=3+4; P, 3 and 4 are operands where as = and + are operator and p=7
is the operation.
Program design tools:
Algorithm, Flow chart and Pseudo
Code
Planning
is the process of finding the steps to solve a problem. It is very important to
solve any problem through computer. A planning indicates the direction of flow
of the process, accurate calculations, points of decisions and other
information in the program. There are three tools of planning to solve
problems. They are:
a) Algorithm:
Algorithm can be defined as a sequence of instructions designed in a manner
that, if the instructions are executes in the specified sequence, the desired
results will be obtained.
Importance /
Characteristics of a good algorithm:
·
Each
and every instruction should be precise and unambiguous.
·
Each
instruction should be performed in a finite time.
·
One
or more instructions should not be repeated infinitely.
·
After
performing the instruction i.e. after the algorithm terminates, the desired
result must be obtained.
Examples of
Algorithm:
Q.N. 1) Write an
algorithm to read two numbers M and N, add them and print the result.
Solution: To solve the
questions
Step
1: Start
Step
2: Read values of two numbers M and N
Step
3: Add M and N
Step
4: Print the sum of M and N
Step
5: Stop
a)
Flow chart:
A flow chart is the diagrammatic or
pictorial representation of procedure proposed to solve problem.
Since it charts flow of program, that’s
why
it is called flow chart.
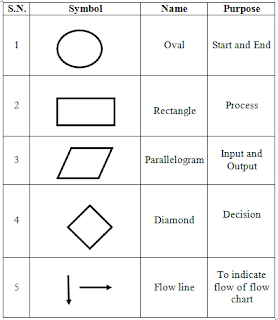
# Symbols used in flow chart
# Advantages of
Flow chart
1.
We
can easily find the relationship between each step.
2.
It
is easy to communicate with facts of problems.
3.
It
is a form of proper program documentation and to modify the programs in future.
4.
With
the help of flowchart coding becomes effective and faster.
5.
It
is easy to make change to the program and it is easy to debug because flow
chart help us to detect, locate and remove logical errors.
# Disadvantages
of the Flow Charts
1.
Flow
charts are waste of time.
2.
It
is slow down process of software development.
3.
It
is quite costly to produce and difficult to use and manage.
4.
Flow
charts are not meant for man to computer communication.
# Rules for
developing Flow chart:
1. The
flow of direction flows from top to bottom or left to right.
2. All
the flow lines must use arrow heads to indicate the flow.
3. Only
one flow line should enter a processing symbol, decision symbol and a terminal
symbol.
4. Flow
line should not cross each other.
5. When
drawing flowchart from one page to another the connector symbol should be
correctly reformed.
Examples:
Flow chart to calculate sum of M and N
a)
Pseudo
code:
Pseudo-code is
a kind of algorithm in which the instructions are expressed in a more English
like structure and mathematical expressions. The instructions of pseudo code
are similar to the program instructions.
Example
of a Pseudo code:
# Pseudo code
to calculate sum of M and N
Start
Input M and N
Sum=M+N
Output Sum
Stop
Program Control
structures: Sequence, Selection and Iteration:
Sequence:
Sequence:
A sequential statement control
structure is a linear structure. It executes statements one after another in a
sequence. There is no mechanism for choosing alternate paths in statement flow.
It executes one statement then automatically moves to next statement and so on.
Flowchart of Sequence:
Selection:
The statement which display one
statement when the condition is true, otherwise display another statement is
known as decision-making statement. Since these statement “control” the flow of
execution, they are also known as control
statement.
C language has following types of
decision making statements are available as follows:
a) Simple if statement
b) if –else statement
c) Nested if-else statement
d) else---if ladder
e) Switch –case statement
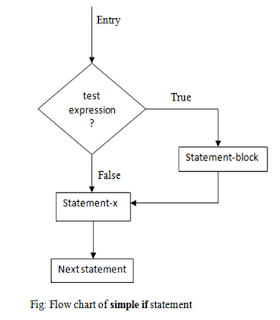
Simple if Statement
The general form of a simple if statement is:
if (test condition)
{
statement-block;
}
statement-x;
Looping:
The
process of executing the same statement repeatedly until a condition is
satisfied is called looping. Every loop has three fundamental components:
initialization, condition and counter. An initialization statement defines the
starting point of the loop. The condition defines the stopping point of the
loop and finally the counter counts the number of iterations. The increment and
decrement operations are used as counter.
If
the task or set of instructions required to be executed “n” number of times, we
can use loop statements.
In
C- language we have 3 types of looping structures.
1.
For
loop
2.
While
loop
3.
Do-while
loop
For Loop
The for loop is
applied in the situation when you exactly know how many times you want to
execute the statements. It is entry-controlled
loop.
Exercise:
Explain the
types of programming errors with examples.
- What is
programming? Differentiate between Compiler and Interpreter.
- What is
Programming language? Explain the types of Programming languages with merits
and demerits.
- Differentiate
between algorithm and flow chart with suitable examples.
- Draw a flowchart
to find the smallest number among any three numbers.
- Define
flowchart. Describe the symbols used in flowchart.
- What is an
Algorithm? Write an algorithm to compute a sales person’s commission based on a
sales volume shown below:
Sales Amount
|
Commission(%
of sales)
|
a)
Under Rs. 500
|
2%
|
b)
Rs.500 or more but under Rs. 5000
|
5%
|
c)
Rs. 5000 and
more
|
10%
|
-0-





Your suggestions / query encourages more to share things like this. Feel free to comment in below box.
What ever you think about it...